The Long Run Average Cost Curve Shows | In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable. If a firm has high fixed costs, increasing output will lead to lower. It is due to economies of scale and diseconomies of scale. The total long run cost function is concave, linear or convex according as the technology displays increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale. Long run average cost is the cost per unit of output feasible when all factors of production are variable. The calculation of the lratc may be represented as a curve showing the lowest costs that a company will be able to reach for any degree of output over time. The total long run cost function is concave, linear or convex according as the technology displays increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale. For relatively small quantities of output, the. Average costs, marginal costs, average variable costs and atc. Graphically, this gives us a lac curve that joins the minimum points of all possible sac curves, as shown in the figure. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible level of. Long run average cost (lac): In this article, we will look at as you can see in the figure above, the long run average cost curve is drawn tangential to all sacs. Long run average cost is the cost per unit of output feasible when all factors of production are variable. The long‐run equilibrium for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is illustrated in figure. The lrac curve assumes that the firm has chosen the optimal factor mix, as described in the previous section, for producing any level of output. Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. It is important to note, however, that this does not mean that the minimum points. Mathematical reason for it being impossible to draw the. The curve avc shows the average variable cost. This lesson introduces you to long run total, marginal and average costs. In the long run, all costs of a firm are variable. In other words, every point on the long run. Average costs, marginal costs, average variable costs and atc. Graphical illustration of long‐run profit maximization. Economies of scale and diseconomies. Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. In the short run, some factors are fixed in the long run, larger output can be produced from large sized plants. In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. The total long run cost function is concave, linear or convex according as the technology displays increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale. The calculation of the lratc may be represented as a curve showing the lowest costs that a company will be able to reach for any degree of output over time. Notice how the average cost is decreasing and the quantity increasing till q3, that. Graphically, this gives us a lac curve that joins the minimum points of all possible sac curves, as shown in the figure. Cm is the minimum cost at which optimum output om can be, obtained. What gives the long run average total cost curve its u shape are the concepts of economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale. Decreasing average fixed costs as output is increased c b. The table below shows how changes in the scale of production can, if increasing returns to scale are exploited the long run average cost curve with economies and diseconomies of scale. We derive it by plugging w ϭ 25 and r ϭ 100 into expression (8.3) to get. Shows the lowest average cost facing a firm as it increases output changing both its plant and labor force. In this article, we will look at as you can see in the figure above, the long run average cost curve is drawn tangential to all sacs. Long run average curve or lac is calculated by dividing total cost in the long run by the level of output. Each average total cost (atc) curve represents a manufacturing scale where the only way to increase output is to hire more workers. What gives the long run average total cost curve its u shape are the concepts of economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible level of. In this video we explore the long run average total cost curve and how average costs vary when all inputs can be adjusted. The calculation of the lratc may be represented as a curve showing the lowest costs that a company will be able to reach for any degree of output over time. The long‐run equilibrium for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is illustrated in figure. Long run average cost curve: Sac, sac1, sac2, sac3 and sac4 are short run average cost curves which. Long run cost refers to the time period in which all factors of production are variable. While history has shown relatively few examples, there are some. Average costs, marginal costs, average variable costs and atc. Graphically, this gives us a lac curve that joins the minimum points of all possible sac curves, as shown in the figure. Notice how the average cost is decreasing and the quantity increasing till q3, that. Mathematical reason for it being impossible to draw the. In other words, every point on the long run. Constant fixed costs as output is increased b. Furthermore, the firm is shown to be producing at the minimum point of its long‐run average total cost curve, at the minimum efficient scale level of. It shows the lowest average total cost to produce a given level of output.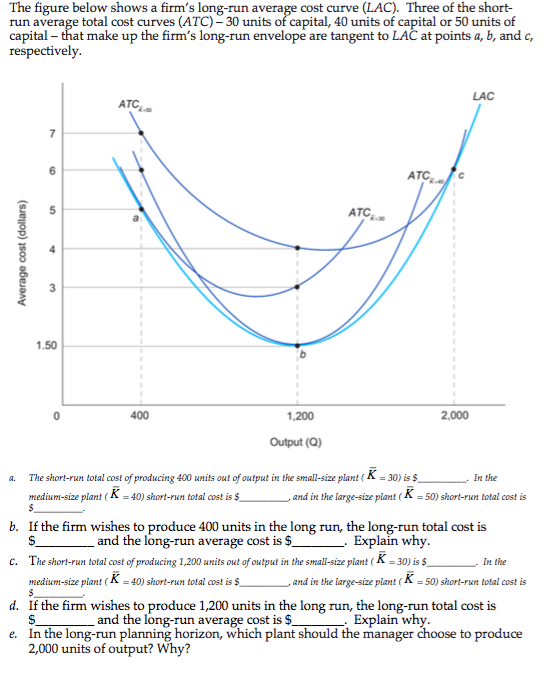

The Long Run Average Cost Curve Shows: The total long run cost function is concave, linear or convex according as the technology displays increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale.
0 comments:
Post a Comment